When dealing with databases, it's crucial to be able to handle and remove duplicates. The DISTINCT statement in MySQL serves precisely this purpose. This blog post will delve into the MySQL DISTINCT statement, providing an in-depth description, syntax, examples, and a summary of its application.
Description
The DISTINCT keyword in MySQL is used to return unique or different values in a SELECT statement. When you have a column with duplicate entries and you want to retrieve only the unique ones, the DISTINCT keyword becomes quite useful.
Note that the DISTINCT keyword considers a whole row as a unit and will not remove duplicates based on one column. If you want to remove duplicates based on a single column, you need to employ a different strategy like using the GROUP BY clause.
Syntax
The basic syntax for the DISTINCT statement in MySQL is as follows:
SELECT DISTINCT column1, column2, ..., columnN
FROM table_name;In this syntax:
column1, column2, ..., columnN: These are the names of the columns in the table from which you want to retrieve unique data.
table_name: This is the name of the table you are selecting data from.
Demo Database
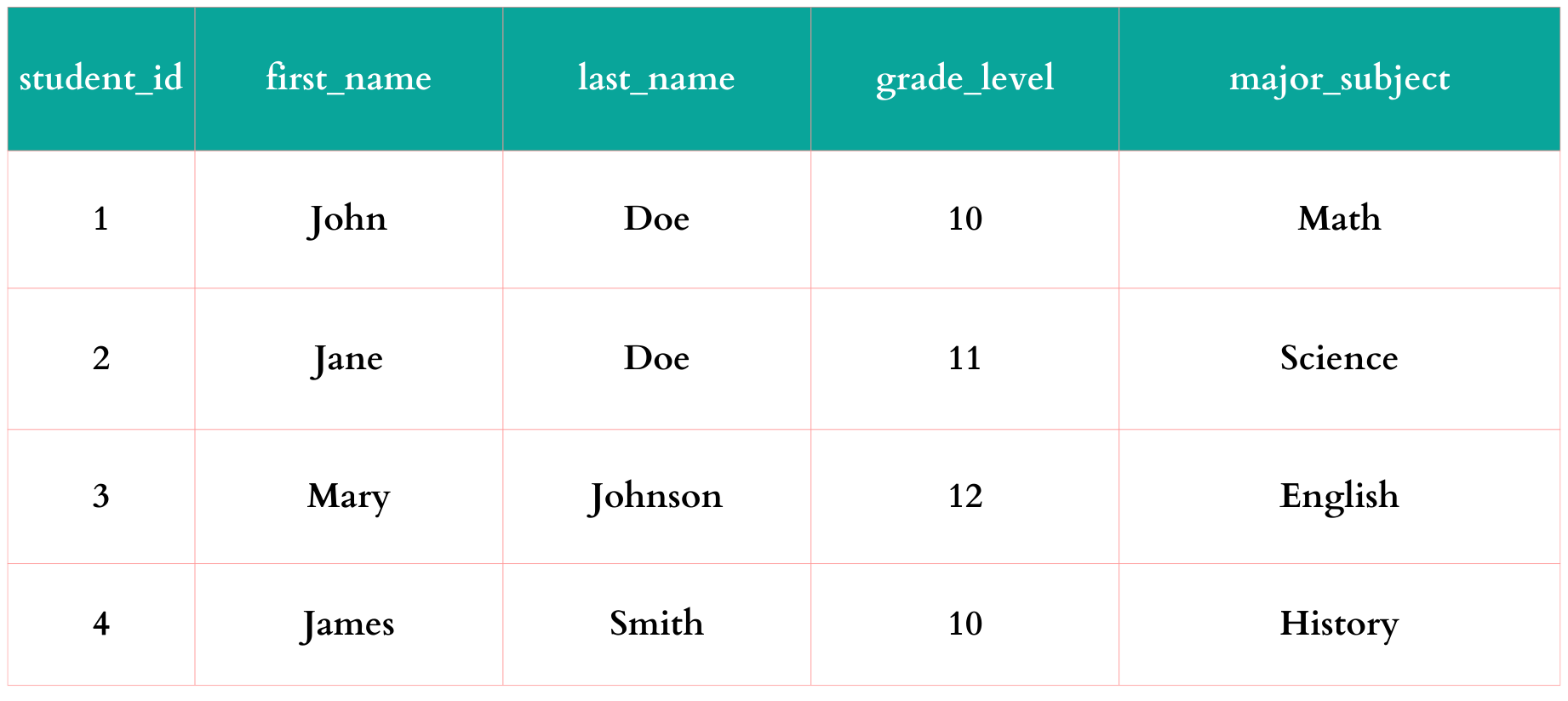
Continuing with our SchoolDB demonstration database, let's focus on the Students table, which includes student_id, first_name, last_name, grade_level, and major_subject columns.Examples
Here are some practical examples illustrating the use of the DISTINCT statement:
Selecting DISTINCT Grades
To retrieve a list of all unique grade_level entries in the Students table:
SELECT DISTINCT grade_level
FROM Students;
Selecting DISTINCT combinations
To retrieve a list of unique grade_level and major_subject combinations in the Students table:SELECT DISTINCT grade_level, major_subject
FROM Students;
Comments
Post a Comment