Prerequisites
Before we start, ensure you have the following:
- Java Development Kit (JDK) installed
- Apache Maven installed
- Node.js and npm installed
- An IDE (such as IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, or VS Code) installed
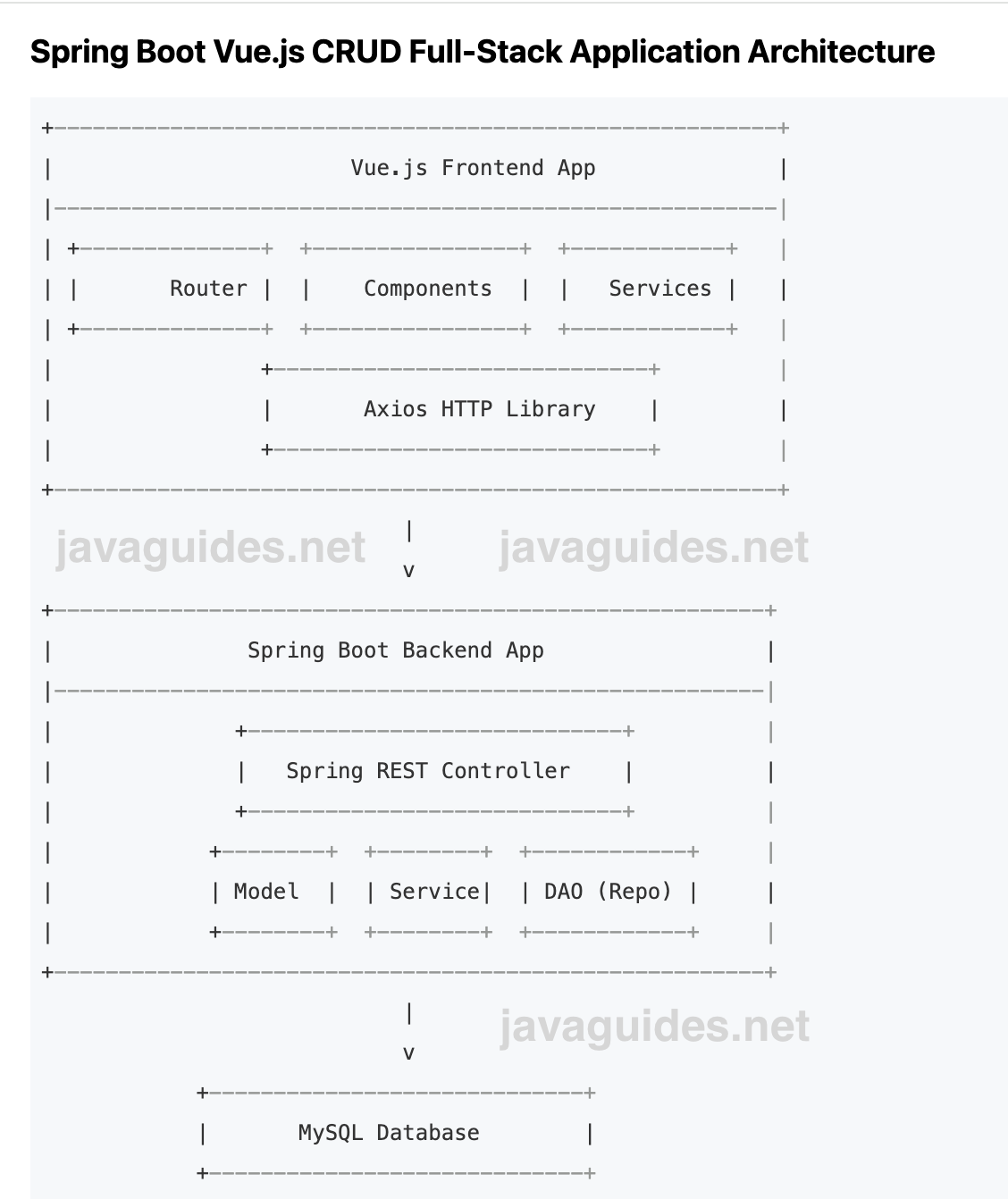
Spring Boot Vue.js CRUD Full-Stack Application Architecture
Explanation:
-
Vue.js Frontend App:
- Router: Manages routing and navigation within the application.
- Components: Represents the UI elements of the application.
- Services: Handles the business logic and data processing in the frontend.
- Axios HTTP Library: A promise-based HTTP client for making requests to the backend.
-
Spring Boot Backend App:
- Spring REST Controller: Handles incoming HTTP requests and defines endpoints.
- Model: Represents the data structure or entity.
- Service: Contains the business logic.
- DAO (Repository): Interacts with the database.
-
MySQL Database: Stores the application's data.
In this architecture, the Vue.js frontend app communicates with the Spring Boot backend app using Axios to make HTTP requests. The backend app processes these requests, interacts with the MySQL database, and sends responses back to the frontend app.
Step 1: Setting Up the Spring Boot Project
1.1 Create a Spring Boot Project
-
Open Spring Initializr:
- Go to Spring Initializr in your web browser.
-
Configure Project Metadata:
- Project: Maven Project
- Language: Java
- Spring Boot: Select the latest version of Spring Boot 3
- Group: com.example
- Artifact: todo-app
- Name: todo-app
- Description: Todo Application with Spring Boot and Vue.js
- Package Name: com.example.todoapp
- Packaging: Jar
- Java Version: 17 (or your preferred version)
- Click
Next.
-
Select Dependencies:
- On the
Dependenciesscreen, select the dependencies you need:- Spring Web
- Spring Data JPA
- H2 Database
- Spring Boot DevTools
- Click
Next.
- On the
-
Generate the Project:
- Click
Generateto download the project zip file. - Extract the zip file to your desired location.
- Click
-
Open the Project in Your IDE:
- Open your IDE and import the project as a Maven project.
1.2 Update application.properties
Open the application.properties file located in the src/main/resources directory and add the following configuration:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
1.3 Create the Todo Entity
In the com.example.todoapp.model package, create a new Java class named Todo:
package com.example.todoapp.model;
import jakarta.persistence.Entity;
import jakarta.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import jakarta.persistence.GenerationType;
import jakarta.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Todo {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
private String description;
private boolean completed;
// Getters and Setters
}
1.4 Create the TodoRepository Interface
In the com.example.todoapp.repository package, create a new Java interface named TodoRepository:
package com.example.todoapp.repository;
import com.example.todoapp.model.Todo;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface TodoRepository extends JpaRepository<Todo, Long> {
}
1.5 Create the TodoService Class
In the com.example.todoapp.service package, create a new Java class named TodoService:
package com.example.todoapp.service;
import com.example.todoapp.model.Todo;
import com.example.todoapp.repository.TodoRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class TodoService {
private final TodoRepository todoRepository;
@Autowired
public TodoService(TodoRepository todoRepository) {
this.todoRepository = todoRepository;
}
public List<Todo> getAllTodos() {
return todoRepository.findAll();
}
public Todo saveTodo(Todo todo) {
return todoRepository.save(todo);
}
public Todo getTodoById(Long id) {
return todoRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
public void deleteTodoById(Long id) {
todoRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
1.6 Create the TodoController Class
In the com.example.todoapp.controller package, create a new Java class named TodoController:
package com.example.todoapp.controller;
import com.example.todoapp.model.Todo;
import com.example.todoapp.service.TodoService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/todos")
public class TodoController {
private final TodoService todoService;
@Autowired
public TodoController(TodoService todoService) {
this.todoService = todoService;
}
@GetMapping
public List<Todo> getAllTodos() {
return todoService.getAllTodos();
}
@PostMapping
public Todo saveTodo(@RequestBody Todo todo) {
return todoService.saveTodo(todo);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Todo getTodoById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return todoService.getTodoById(id);
}
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public void deleteTodoById(@PathVariable Long id) {
todoService.deleteTodoById(id);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public Todo updateTodo(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Todo todo) {
Todo existingTodo = todoService.getTodoById(id);
if (existingTodo != null) {
existingTodo.setTitle(todo.getTitle());
existingTodo.setDescription(todo.getDescription());
existingTodo.setCompleted(todo.isCompleted());
return todoService.saveTodo(existingTodo);
} else {
return null;
}
}
}
Step 2: Creating the Frontend with Vue.js
2.1 Set Up Vue Project
-
Open a terminal and navigate to your workspace directory.
-
Create a new Vue project using Vue CLI:
npm install -g @vue/cli vue create vue-frontend -
Navigate to the project directory:
cd vue-frontend
2.2 Install Axios
Install Axios to make HTTP requests:
npm install axios
2.3 Create Components
Create the necessary components for displaying and managing todos.
2.3.1 Create TodoService.js
Create a new file TodoService.js in the src directory to handle API requests for todos:
import axios from 'axios';
const API_BASE_URL = "http://localhost:8080/todos";
class TodoService {
getAllTodos() {
return axios.get(API_BASE_URL);
}
getTodoById(todoId) {
return axios.get(`${API_BASE_URL}/${todoId}`);
}
createTodo(todo) {
return axios.post(API_BASE_URL, todo);
}
updateTodo(todo) {
return axios.put(`${API_BASE_URL}/${todo.id}`, todo);
}
deleteTodo(todoId) {
return axios.delete(`${API_BASE_URL}/${todoId}`);
}
}
export default new TodoService();
2.3.2 Create TodoListComponent.vue
Create a new file TodoListComponent.vue in the src/components directory:
<template>
<div>
<h2>Todos</h2>
<ul>
<li v-for="todo in todos" :key="todo.id">
{{ todo.title }} - {{ todo.description }} - {{ todo.completed ? 'Completed' : 'Not Completed' }}
<button @click="editTodo(todo)">Edit</button>
<button @click="deleteTodo(todo.id)">Delete</button>
</li>
</ul>
<div v-if="editingTodo">
<h3>Edit Todo</h3>
<form @submit.prevent="updateTodo">
<input v-model="editingTodo.title" placeholder="Todo Title" />
<input v-model="editingTodo.description" placeholder="Todo Description" />
<label>
Completed:
<input type="checkbox" v-model="editingTodo.completed" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Update</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TodoService from '../TodoService';
export default {
data() {
return {
todos: [],
editingTodo: null
};
},
created() {
this.fetchTodos();
},
methods: {
fetchTodos() {
TodoService.getAllTodos().then(response => {
this.todos = response.data;
});
},
editTodo(todo) {
this.editingTodo = { ...todo };
},
updateTodo() {
TodoService.updateTodo(this.editingTodo).then(() => {
this.fetchTodos();
this.editingTodo = null;
});
},
deleteTodo(todoId) {
TodoService.deleteTodo(todoId).then(() => {
this.fetchTodos();
});
}
}
};
</script>
2.3.3 Create AddTodoComponent.vue
Create a new file AddTodoComponent.vue in the src/components directory:
<template>
<div>
<h2>Add Todo</h2>
<form @submit.prevent="
addTodo">
<input v-model="todo.title" placeholder="Todo Title" />
<input v-model="todo.description" placeholder="Todo Description" />
<label>
Completed:
<input type="checkbox" v-model="todo.completed" />
</label>
<button type="submit">Add</button>
</form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TodoService from '../TodoService';
export default {
data() {
return {
todo: {
title: '',
description: '',
completed: false
}
};
},
methods: {
addTodo() {
TodoService.createTodo(this.todo).then(() => {
this.todo.title = '';
this.todo.description = '';
this.todo.completed = false;
});
}
}
};
</script>
2.3.4 Create App.vue
Modify the App.vue file to include routing for the components:
<template>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<router-link to="/">Todos</router-link>
<router-link to="/add-todo">Add Todo</router-link>
</nav>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
};
</script>
<style>
nav {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
2.3.5 Update main.js
Ensure the main.js file is set up correctly:
import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router';
import TodoListComponent from './components/TodoListComponent.vue';
import AddTodoComponent from './components/AddTodoComponent.vue';
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: TodoListComponent },
{ path: '/add-todo', component: AddTodoComponent }
];
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHistory(),
routes
});
const app = createApp(App);
app.use(router);
app.mount('#app');
Step 3: Running the Application
3.1 Run the Spring Boot Application
- Open the
TodoAppApplicationclass in thesrc/main/java/com/example/todoappdirectory. - Click the green
Runbutton in your IDE or use the terminal to run the application:./mvnw spring-boot:run
3.2 Run the Vue.js Application
-
Open a terminal and navigate to the
vue-frontenddirectory. -
Start the Vue application:
npm run serve -
Open your web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:8080.
You should now be able to view, add, update, and delete todos using the Vue.js frontend and Spring Boot backend.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we created a full-stack application using Spring Boot for the backend and Vue.js for the frontend. We implemented CRUD operations and handled the necessary configurations to connect the two parts of the application. This setup provides a solid foundation for developing more complex full-stack applications.

Comments
Post a Comment